Oil Soars Past $100 After Russia Attacks Ukraine

[Stay on top of transportation news: Get TTNews in your inbox.]
Oil surged above $105 a barrel for the first time since 2014 after Russia attacked sites across Ukraine, triggering fears of a disruption to energy exports at a time of already tight supplies.
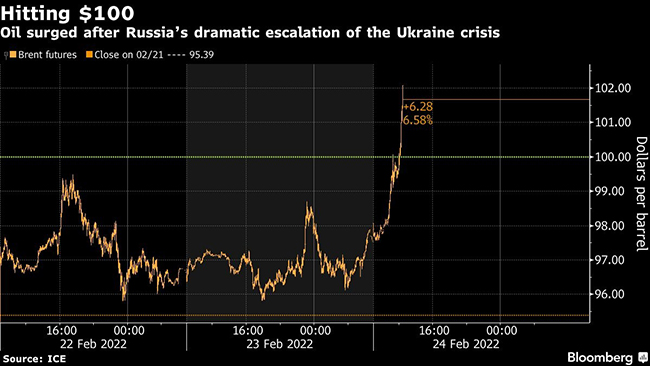
Brent was up about 6%, paring gains after surging as much 9.2% to $105.79 a barrel after President Vladimir Putin ordered Russian troops into Ukraine. U.S. benchmark West Texas Intermediate briefly topped $100 a barrel before easing off of gains at the open in New York. Kyiv called it a “full-scale invasion” and announced martial law, while U.S. President Joe Biden said he would impose “severe sanctions” on Moscow.
Russia is a key supplier of energy to global customers, with Europe relying on the nation for about a quarter of its oil supplies and a third of its gas.
The escalation spooked a market that was already under stress, as oil supplies around the world fail to keep pace with the vigorous recovery in demand from the pandemic. The OPEC+ coalition led by Saudi Arabia is struggling to restore production quickly enough, prompting some of the biggest market players to warn of an increasingly tight market.
“A further escalation has pushed prices to the $100-a-barrel mark,” said Warren Patterson, head of commodities strategy at ING Groep NV. “The oil market will now wait to see how Western nations respond to Russia’s latest actions. As a result, we will likely see even further volatility in the market, as well as the need to price in a larger risk premium.”
Oil prices are likely to average $110 in the second quarter as tensions over Ukraine continue to escalate, JPMorgan Chase & Co. said this week before the latest escalation. The crude market is likely to see sustained higher prices in the next quarter, before retreating to average $90 at the end of the year, according to the bank.
The Biden administration is considering tapping its emergency supply of oil again in coordination with allies to counter the surge in prices brought on by Russia’s moves against Ukraine. The White House earlier announced sanctions on some Russian banks, sovereign debt and elites.
The April contract for Brent was at $101.51 a barrel at 12:39 p.m. Singapore time Feb. 24 (11:39 p.m. EST Feb. 23) after briefly touching its intraday high of $102.08. West Texas Intermediate was at $96.11 a barrel.
Crude’s return to triple digits completes a prodigious recovery — barely imaginable a year ago — as the market flips from surplus to scarcity. It reflects a global economy rushing back to normality from COVID-19 faster than it can secure supplies of raw materials of all kinds.
“As demand recovers to pre-COVID levels, supply is really having a hard time,” said Giovanni Serio, global head of market analysis at Vitol Group, the world’s biggest independent oil trader.
In addition to oil and gas, Russia is a major producer of aluminum and wheat, which Ukraine also grows. The increase in the price of multiple commodities is contributing to a surge in inflation to the highest level in decades, threatening a cost-of-living crisis for millions and forcing central banks to contemplate a phase of monetary tightening that might choke off the rebound.
“Oil prices continue to surge and are now reaching levels that are uncomfortable for consumers across the world,” Toril Bosoni, head of the International Energy Agency’s markets and industry division, said in a Bloomberg Television interview. “The oil market is incredibly tight.”
While it’s a pressing concern for all consuming nations, the rally has been a particular source of discomfort for Biden, whose attempts to rein in soaring fuel costs ahead of this year’s midterm elections by deploying emergency stockpiles have met with little success.
Biden has pledged to “work like the devil” to get fuel costs under control, stressing the importance of energy security during a recent call with Saudi King Salman bin Abdulaziz.
Want more news? Listen to today's daily briefing above or go here for more info
The OPEC+ alliance led by Saudi Arabia and Russia is at the heart of the supply crunch. Besides Riyadh and its Gulf neighbors, under-investment and unrest are preventing several members from reviving output halted during the pandemic. The group delivered only 70% of last month’s scheduled boost, according to the IEA.
Their shortcomings are creating a further source of anxiety: that the spare capacity left to fill in for any disruptions — whether deeper losses in conflict-torn Libya, or from further drone strikes in Abu Dhabi — has dwindled to dangerously low levels.
“I’m not necessarily thinking that OPEC is in control of things any more,” said Torbjorn Tornqvist, chief executive officer of commodity-trading house Gunvor Group Ltd. “We’re back in a situation where we’re watching what the spare capacity is going to be.”
Supply constraints go beyond the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries and its partners. Investment in new supplies worldwide has contracted as a result of the COVID slump and a diversion of capital away from fossil fuels toward renewable energy. In the U.S., once-prolific shale explorers have reined in spending to pay back shareholders.




